
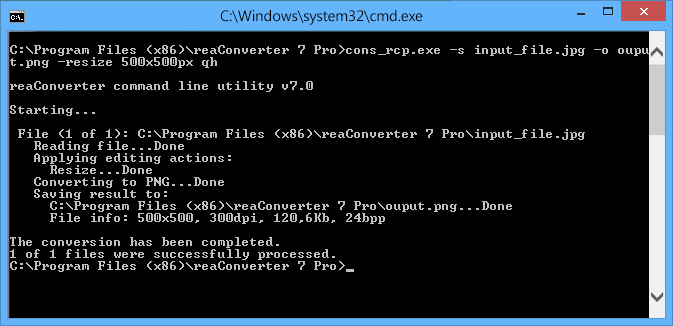
Security ID: WIN-R9H529RIO4Y\Administrator Process Command Line: Pre-Windows 2016/10 Mandatory Label: Mandatory Label\Medium Mandatory LevelĬreator Process Name: C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe New Process Name: C:\Windows\System32\RuntimeBroker.exe See “Administrative Templates\System\Audit Process Creation\Include command line in process creation events” in group policy.
#CMD C START LOW WINDOWS#
Mandatory Label: (new to Win10) In addition to each objects Discretionary Access Control List (permissions on a file) Windows also enforces Mandatory Integrity Control (MIC) over object access attempts which compares the object's integrity label to the the integrity level on the process trying to access the object.The limited token is used when User Account Control is enabled, the application does not require administrative privilege, and the user does not choose to start the program using Run as administrator. It's a limited token with administrative privileges removed and administrative groups disabled. %% 1938 - Type 3 is the normal value when UAC is enabled and a user simply starts a program from the Start Menu.An elevated token is also used when an application is configured to always require administrative privilege or to always require maximum privilege, and the user is a member of the Administrators group. An elevated token is used when User Account Control is enabled and the user chooses to start the program using Run as administrator.
%% 1937 - Type 2 is an elevated token with no privileges removed or groups disabled.
#CMD C START LOW FULL#
A full token is only used if User Account Control is disabled or if the user is the built-in Administrator account or a service account.

New Process Name: The full path of the executable.To determine when the program ended look for a subsequent event 4689 with the same Process ID. Process ID allows you to correlate other events logged during the same process. New Process ID: A semi-unique (unique between reboots) number that identifies the process.One of the examples below shows the SYSTEM account starting RuntimeBroker.exe as a different user. By default, a new process runs under the same account and logon session as the creator process. These fields only apply when the process is started under a different user account. Logon ID allows you to correlate backwards to the logon event (4624) as well as with other events logged during the same logon session.Īdded in Win2016/10. Logon ID: A semi-unique (unique between reboots) number that identifies the logon session.Account Domain: The domain or - in the case of local accounts - computer name.The user and logon session that started the program.
#CMD C START LOW FREE#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
